If you’ve browsed hosting plans or VPS providers, you’ve probably come across the term CentOS. Many hosting companies list it as an available operating system for servers. But what exactly is CentOS, and why is it so popular in the hosting world?
In this article, we’ll explain CentOS in the simplest terms, its history, strengths, limitations, and its role in web hosting today.
What is CentOS?
CentOS stands for Community Enterprise Operating System.
It’s a free, open-source Linux distribution built from the source code of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), which is a paid enterprise operating system.
Think of it this way:
- RHEL is the official, enterprise-grade, paid version.
- CentOS is the free version with the same core features, maintained by the community, but without Red Hat’s commercial support.
Because of its stability and zero licensing costs, CentOS became one of the most widely used systems in the web hosting and server industry.

A Quick History of CentOS
| Year | Key Event |
|---|---|
| 2004 | CentOS was launched as a free rebuild of RHEL. |
| 2009-2011 | Rapid growth, with CentOS 5.4 and 6 gaining popularity in enterprises. |
| 2014 | Red Hat acquired CentOS, integrating it more closely with RHEL development. |
| 2019 | CentOS Stream was introduced as a rolling-release preview of future RHEL updates. |
| 2020-2021 | CentOS 8 released. Red Hat announced traditional CentOS Linux would be phased out, shifting focus to CentOS Stream. This led to the creation of Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux as direct replacements. |
Why Is CentOS Popular in Hosting?
1. Stability and Reliability
CentOS is known for being extremely stable. It’s built from RHEL, which is trusted by large enterprises for critical infrastructure.
For hosting companies, this means:
- Servers run smoothly with minimal crashes.
- Customer websites experience less downtime, leading to better trust and satisfaction.
2. Free and Cost-Effective
While RHEL requires expensive annual licensing fees, CentOS offers almost identical performance for free.
Hosting companies can deploy thousands of CentOS-based servers without licensing costs, allowing them to offer affordable VPS and dedicated hosting plans to customers.
3. High Compatibility with Hosting Tools
CentOS works seamlessly with the most popular hosting control panels:
- cPanel / WHM
- Plesk
- DirectAdmin
Most hosting software is developed and tested primarily on CentOS and RHEL, ensuring optimal performance and easy setup.
4. Strong Security
CentOS integrates SELinux (Security Enhanced Linux), providing advanced security policies to protect servers against hacking and malware attacks.
Additionally, the CentOS community quickly releases patches to address vulnerabilities, keeping hosting environments safe.
5. Large Community Support
Although CentOS doesn’t have paid support like RHEL, it has a huge global community.
This means:
- Tons of tutorials, documentation, and forums for troubleshooting.
- Quick answers for server administrators and hosting providers.
How Is CentOS Used in Hosting?
VPS Hosting
Most VPS providers (e.g. DigitalOcean, Linode, Hostinger) offer CentOS as a default or recommended OS due to its stability and compatibility with hosting control panels.
Web Servers
Hosting companies use CentOS for their backend servers to host websites built with WordPress, Magento, Drupal, and more.
Database Servers
CentOS runs MySQL, MariaDB, and PostgreSQL efficiently, making it suitable for hosting databases that power client websites and apps.
Private Cloud and Virtualization
Companies use CentOS with virtualization technologies like KVM and cloud platforms like OpenStack to deploy scalable cloud solutions.
What is CentOS Stream?
In 2019, CentOS Stream was introduced as a rolling-release version of CentOS. It acts as a preview of upcoming RHEL features.
| Traditional CentOS | CentOS Stream |
|---|---|
| Stable, minimal updates | Rolling updates, more frequent changes |
| Ideal for production environments | Ideal for development and testing |
| Direct rebuild of RHEL | Sits between Fedora (newest) and RHEL (stable) |
Why the change?
In 2020, Red Hat announced they would stop maintaining traditional CentOS Linux, shifting focus to CentOS Stream. While Stream is great for previewing new features, many hosting providers prefer maximum stability.
As a result, two CentOS alternatives emerged:
- Rocky Linux – led by CentOS’s original founder, aims to continue CentOS’s original mission.
- AlmaLinux – backed by CloudLinux, also fully compatible with RHEL.
CentOS vs. Ubuntu: Which Is Better for Hosting?
| Feature | CentOS (Rocky/Alma) | Ubuntu |
|---|---|---|
| Stability | Extremely high | High, with faster updates |
| Ease of use | More technical | Beginner-friendly |
| Control panel support | Excellent (cPanel, WHM) | Excellent (cPanel supports Ubuntu 20.04+) |
| Popularity in hosting | High among traditional hosting providers | Very high, most popular in VPS and cloud |
| Ideal for | Enterprise servers, hosting providers needing RHEL compatibility | Servers, desktops, developers, cloud hosting |
✅ Choose CentOS if you need stability, compatibility with traditional hosting tools, and enterprise-level security.
✅ Choose Ubuntu if you prefer ease of use, faster software versions, or a more desktop-like experience.
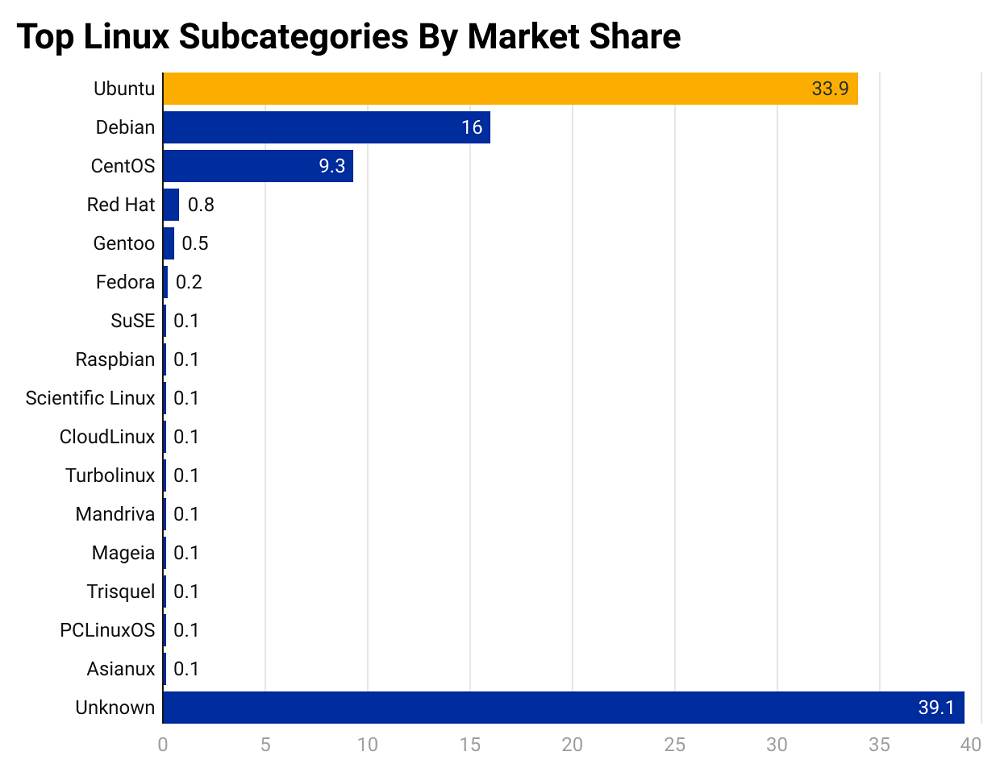
source: Sci-Tech Today
Although traditional CentOS Linux has ended, CentOS Stream continues as a development-focused distribution. For hosting companies and users needing the same reliability as before, Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux are now the main replacements.
Both are:
- Free and open-source
- Compatible with RHEL software
- Supported by strong communities
Final Thoughts
CentOS has been a pillar of the hosting industry for almost two decades, powering millions of websites worldwide with its stability, security, and performance.
Today, while CentOS Stream serves a new role, Rocky Linux and AlmaLinux continue its legacy, providing hosting providers and server administrators with the robust, cost-effective Linux environment they rely on.
